Apart from the principle missions assigned to the HRVIRs (1) and
Vegetation (7) other technological or scientific instruments will be carried by
SPOT 4.
 (6)
- DORIS (Détermination d'Orbite
et Radio Positionnement Intégrés par Satellite
- Doppler Orbitography and Radiopositioning Integrated by Satellite) identical to the
instruments carried by previous SPOT satellites. This system, tested since SPOT 2,
uses ground processing to determine the satellite's position to within 10 cm. It can also
be used to locate ground beacons with the same accuracy. On SPOT 4, complementary onboard
software will be tested (the DIODE experiment) for
real-time calculation of the satellite's position, to within about 20 metres, using data
provided by DORIS. This position will be sent in the auxiliary data which accompany the
image telemetry.
(6)
- DORIS (Détermination d'Orbite
et Radio Positionnement Intégrés par Satellite
- Doppler Orbitography and Radiopositioning Integrated by Satellite) identical to the
instruments carried by previous SPOT satellites. This system, tested since SPOT 2,
uses ground processing to determine the satellite's position to within 10 cm. It can also
be used to locate ground beacons with the same accuracy. On SPOT 4, complementary onboard
software will be tested (the DIODE experiment) for
real-time calculation of the satellite's position, to within about 20 metres, using data
provided by DORIS. This position will be sent in the auxiliary data which accompany the
image telemetry.
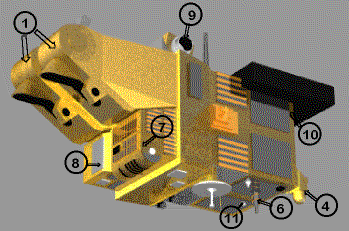
(10) - ESBT (Experimental S--Band
Terminal) is the counterpart of PASTEL, but concerns SPOT 4 command
and control functions. Exchanges will take place via Artemis, a relay satellite, with a
slower transmission rate than that of PASTEL. However, it will enable much longer
satellite visibility windows than those offered by the 2 Ghz TT&C stations. Safety and
ease of operation will therefore be greatly increased with this type of instrument.
(9) - PASTEL (PAssager SPOT
de TElécommunication Laser - SPOT Passenger for Laser
Telecommunications) which is part of the SILEX (Semiconductor Intersatellite
Link EXperiment) European Space Agency experiment.
PASTEL will enable high speed transmission of imagery to the ground segment. This will be
done on an optical channel, via the geostationary relay satellite, Artemis which is to be
launched at the beginning of 2001.
(8) - PASTEC (PASsager TEChnologique
), designed to study the orbital environment. This is a set of technological experiments
to confirm knowledge in areas such as ageing of materials, launch vibrations, etc.
(4) - POAM III (Polar Ozone
and Aerosol Measurement), an experiment to be conducted
by the United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) to measure the vertical distribution
of atmospheric components by solar occultation.
(11) VEGA, a radar transponder, used on all SPOT family satellites to
calibrate ground radars.
top of page, article

page updated on the 00-06-06
 (6)
- DORIS (Détermination d'Orbite
et Radio Positionnement Intégrés par Satellite
- Doppler Orbitography and Radiopositioning Integrated by Satellite) identical to the
instruments carried by previous SPOT satellites. This system, tested since SPOT 2,
uses ground processing to determine the satellite's position to within 10 cm. It can also
be used to locate ground beacons with the same accuracy. On SPOT 4, complementary onboard
software will be tested (the DIODE experiment) for
real-time calculation of the satellite's position, to within about 20 metres, using data
provided by DORIS. This position will be sent in the auxiliary data which accompany the
image telemetry.
(6)
- DORIS (Détermination d'Orbite
et Radio Positionnement Intégrés par Satellite
- Doppler Orbitography and Radiopositioning Integrated by Satellite) identical to the
instruments carried by previous SPOT satellites. This system, tested since SPOT 2,
uses ground processing to determine the satellite's position to within 10 cm. It can also
be used to locate ground beacons with the same accuracy. On SPOT 4, complementary onboard
software will be tested (the DIODE experiment) for
real-time calculation of the satellite's position, to within about 20 metres, using data
provided by DORIS. This position will be sent in the auxiliary data which accompany the
image telemetry.