POAM III
Science Channels
 The
Polar Ozone and Aerosol Measurement III (POAM III) instrument was developed by the
Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) to measure the vertical distribution of atmospheric ozone,
water vapor, nitrogen dioxide, aerosol extinction, and temperature.
The
Polar Ozone and Aerosol Measurement III (POAM III) instrument was developed by the
Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) to measure the vertical distribution of atmospheric ozone,
water vapor, nitrogen dioxide, aerosol extinction, and temperature.
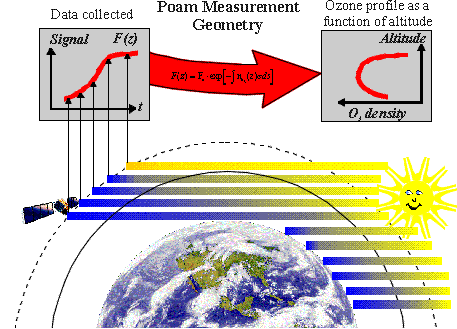
Measurements are made using the solar occultation technique; the Sun is observed through
the Earth's atmosphere as it rises and sets as viewed from the satellite. Solar extinction
is measured in nine narrow band optical channels, covering the spectral range from
350 to 1030 nm
POAM III is an improved version of POAM II. It has an improved
electronic system that provides lower noise and more accurate measurements. The optical
filters were manufactured with a better technology that yields higher transmission and
greater ability to withstand the space environment. The wavelenths and bandwidths of the
science channels differ slightly from those in POAM II. POAM III, like
POAM II, was fabricated by ThermoTrex
Corporation in San Diego, California.
top of page, article
| Channel |
Center Wavelength
(nm) |
Width (nm) |
Primary Purpose |
| 1 |
353.4 |
9.70 |
Rayleigh scattering |
| 2 |
439.7 |
2.07 |
NO2 present |
| 3 |
442.3 |
2.05 |
NO2 absent |
| 4 |
603.4 |
17.7 |
Ozone |
| 5 |
761.3 |
2.25 |
Oxygen present |
| 6 |
779.4 |
10.1 |
Oxygen absent, Aerosol |
| 7 |
922.4 |
2.56 |
H2O absent, Aerosol |
| 8 |
935.8 |
2.59 |
H2O present |
| 9 |
1018.5 |
11.5 |
Aerosol |
POAM III was launched on the French SPOT 4 satellite
into a Sun-synchronous polar orbit, in March 1998. As seen from the satellite, the Sun
rises in the north polar region and sets in the south polar region 14.2 times per day.
Sunrise measurements are made in a latitude band from 55 to 71 degrees north while sunsets
occur between 63 to 88 degrees south.
Further details about the POAM II instrument can be found in Glaccum, et al. [1996].
The retrieval process is described by Lumpe et al., [JGR, 1997]. The POAM
measurements have been applied to studies of ozone in the Antarctic [Bevilacqua et al.,
1995 and 1996], and the Arctic [Randall et al., 1995]. Intercomparisons of the POAM
ozone measurements have been made with the CIRA ozone models, [Shettle et al.,
1995], ozonesondes, [Deniel et al. , JGR, 1997], and other satellites, [Rusch et
al., JGR, 1997]. Preliminary results of the POAM aerosol measurements are presented in
Brogniez, et al. [1996], and in Randall et al. [1996]. POAM has also been
applied to the study of Polar Mesospheric Clouds [Debrestian et al., 1996], and the
study of Polar Stratospheric Clouds [Fromm et al., JGR, 1997].
[Publication list]
top of page, article

page updated on the 00-06-06
 The
Polar Ozone and Aerosol Measurement III (POAM III) instrument was developed by the
Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) to measure the vertical distribution of atmospheric ozone,
water vapor, nitrogen dioxide, aerosol extinction, and temperature.
The
Polar Ozone and Aerosol Measurement III (POAM III) instrument was developed by the
Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) to measure the vertical distribution of atmospheric ozone,
water vapor, nitrogen dioxide, aerosol extinction, and temperature. 